Description
What our Human Ear lesson plan includes
Lesson Objectives and Overview: Human Ear teaches students all about the parts and functions of ears. Students will discover how the three main parts of an ear have separate functions and shared responsibilities. They will also learn how the ear works to help us register and understand sound waves. This lesson is for students in 4th grade, 5th grade, and 6th grade.
Classroom Procedure
Every lesson plan provides you with a classroom procedure page that outlines a step-by-step guide to follow. You do not have to follow the guide exactly. The guide helps you organize the lesson and details when to hand out worksheets. It also lists information in the yellow box that you might find useful. You will find the lesson objectives, state standards, and number of class sessions the lesson should take to complete in this area. In addition, it describes the supplies you will need as well as what and how you need to prepare beforehand.
Options for Lesson
In the “Options for Lesson” section of the classroom procedure page, you will find a few more ideas or suggestions for additional activities or assignments. If you have time or want to extend the lesson, feel free to incorporate any of these options into the lesson plan. One option is to create an assignment in which students research the ears of an animal and find out how that animal hears sounds. (You could have students choose their own animal if you wish.) Another option is to have students research hearing aids and how they improve sound for those people who use them. One more idea is to use the sound from loud speakers to show sound waves.
Teacher Notes
The paragraph on this page provides a little more information or guidance on what to expect from the lesson. It mentions the value in using additional resources and activities. You may also benefit from adding a discussion about how hearing aids work for those with hearing difficulties. You can use the blank lines to record any thoughts you ideas you have as you prepare.
HUMAN EAR LESSON PLAN CONTENT PAGES
Outer Ear
The Human Ear lesson plan has two content pages. It first presents an image of a man holding his hand up to his ear as if to ask, “What did you say? Please speak louder.” Without those things on the side of the head called ears, we would not be able to hear anything. We wouldn’t hear someone saying our name, the sound of a phone ringing, or music. The human ear, though, is not just for hearing; it also helps with balance. There are three main parts of the ear: outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. And each part has a shared responsibility.
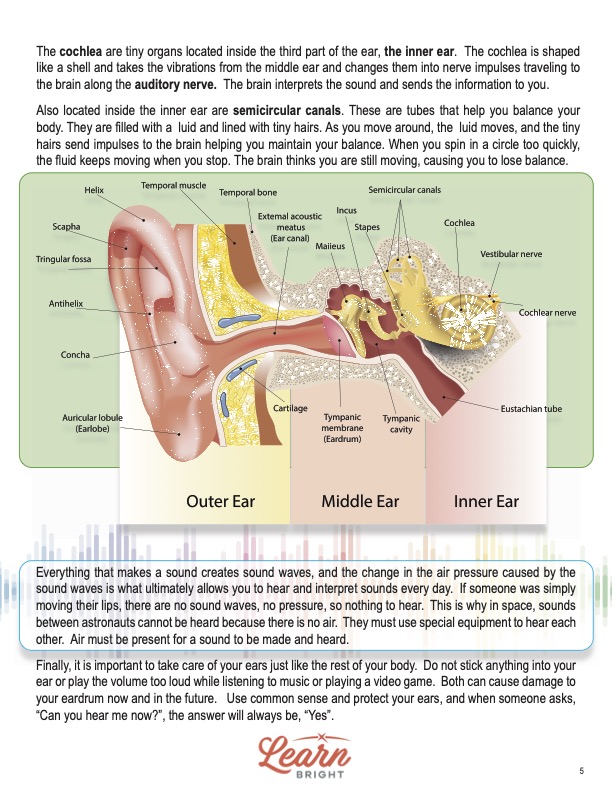
The outer ear is the part we can see in the mirror, scratch, or clean behind. Students will learn that the ear is also called the pinna. Ears are made of cartilage covered by skin, which includes a part called the ear lobe. The outer ear contains the ear canal as well, which is similar to a canal for water. However, this canal is a pathway for all the sounds in the environment to enter.
Speaking of the canal, the lining of the canal is the place earwax is produced. Earwax helps keep the eardrum from drying out. In addition, the wax traps dirt before it gets to the eardrum and causes an infection. When it comes to hearing, the outer ear catches the sound waves and funnels them to the eardrum, where the middle ear is located.
Middle and Inner Ear
The middle ear is basically air-filled space inside the eardrum. For proper hearing, the pressure placed on both sides of the eardrum must be equal. If the pressure is not equal, our ears may pop, which is what happens on an airplane or at the swimming pool. The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and helps keep the pressure equal.
There are three bones inside the eardrum called ossicles (which rhymes with popsicles). These tiny bones include the hammer (malleus), anvil (incus), and stirrup (stapes). The names of each of these bones match what they look like. The stirrup is the smallest bone of the entire human body. Once sound waves enter the eardrum, these bones pass along the vibrations to the cochlea.
A cochlea is a tiny organ inside the third part of the ear, the inner ear. It is shaped like a shell and takes the vibrations from the middle ear and changes them into nerve impulses that travel to the brain along the auditory nerve. The brain interprets the sound and sends the information to us.
Also located inside the inner ear are semicircular canals. These are tubes that help us balance our body. They are filled with a kind of fluid and lined with tiny hairs. As we move around, the fluid moves, and the tiny hairs send impulses to the brain to help us maintain balance. When we spin in a circle too quickly and stop suddenly, the fluid keeps moving when we stop. The brain thinks we are still moving, and this is what causes us to lose balance.
Taking Care of the Ears
Everything that makes a sound creates sound waves. The change in the air pressure caused by the sound waves is what ultimately allows us to hear and interpret sounds every day. If someone simply moves their lips, they produce no sound waves and no pressure. In this case, there is nothing to hear. This is why, in space, sounds between astronauts are inaudible because there is no air. They must use special equipment to hear each other. Air must be present to produce and hear sounds.
Finally, it is important to take care of the ears just like the rest of the body. For instance, it’s not a good idea to stick things into the ear or have the volume too high while listening or watching something. Both of these actions can cause damage to our eardrums now and in the future. It’s important to use common sense and protect our ears. That way, when someone asks, “Can you hear me now?”, the answer will always be, “Yes!”
HUMAN EAR LESSON PLAN WORKSHEETS
The Human Ear lesson plan includes three worksheets: an activity worksheet, a practice worksheet, and a homework assignment. Each worksheet helps reinforce the lesson concepts and allows students to demonstrate what they learned in different ways. You can refer to the guide on the teacher notes page to determine when to hand out each worksheet to the students.
HEARING EXPERIMENT ACTIVITY WORKSHEET
The activity requires students to conduct an experiment that tests how easy it is to hear with one ear versus two. Students will use the supplies in the materials list to conduct the experiment. To set up, you and the students will first place a chair at the end of a large room. Then you will mark an ‘X’ every five feet from the chair until you reach a distance of 25 feet.
Have one volunteer sit in the chair, and blindfold them so they cannot see. Put an earplug in one of their ears. Have other students randomly choose an ‘X’ to stand on and play a specific sound for five seconds. The volunteer sitting down will then guess how far away the student is who played the sound.
As a class, you will repeat steps five through seven up to 20 times. Then the volunteer will remove the earplug. At that point, repeat steps five through seven another dozen or so times. When you have completed the experiment as many times as you wish, have students answer the questions at the bottom of the activity worksheet.
SOUND WAVES EXPERIMENT PRACTICE WORKSHEET
For the practice worksheet, students will conduct another experiment to test how sound waves work. Using the supplies you provide, they will create an “eardrum” using a bowl and plastic wrap. They will stretch the plastic over the large round container as tightly as possible. Then they will place around 50 grains of dry rice on the plastic.
Standing close to the container, they will make a loud noise with a handbell or by banging two metal pans together. They will then record their observations in the first box on the worksheet. After moving about five feet away, they will make another loud noise and record their observations.
HUMAN EAR HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT
The homework assignment spans three pages. There are 21 questions total that students must answer. Once again, you can decide whether or not students can refer to the content pages for help as they work on this assignment.
Worksheet Answer Keys
The last several pages of the lesson PDF are answer keys. All the correct answers are in red to make it easy to compare them to students’ work. Given the nature of the worksheets, there should be no variation in students’ responses. If you choose to administer the lesson pages to your students via PDF, you will need to save a new file that omits these pages. Otherwise, you can simply print out the applicable pages and keep these as reference for yourself when grading assignments